As autonomous vehicles continue to evolve, the need for accurate and high-quality training data has never been more critical. Two of the most widely used data sources in autonomous driving systems are LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) and camera data. While both play vital roles, they offer different types of information—and understanding these differences is crucial for data annotators. 
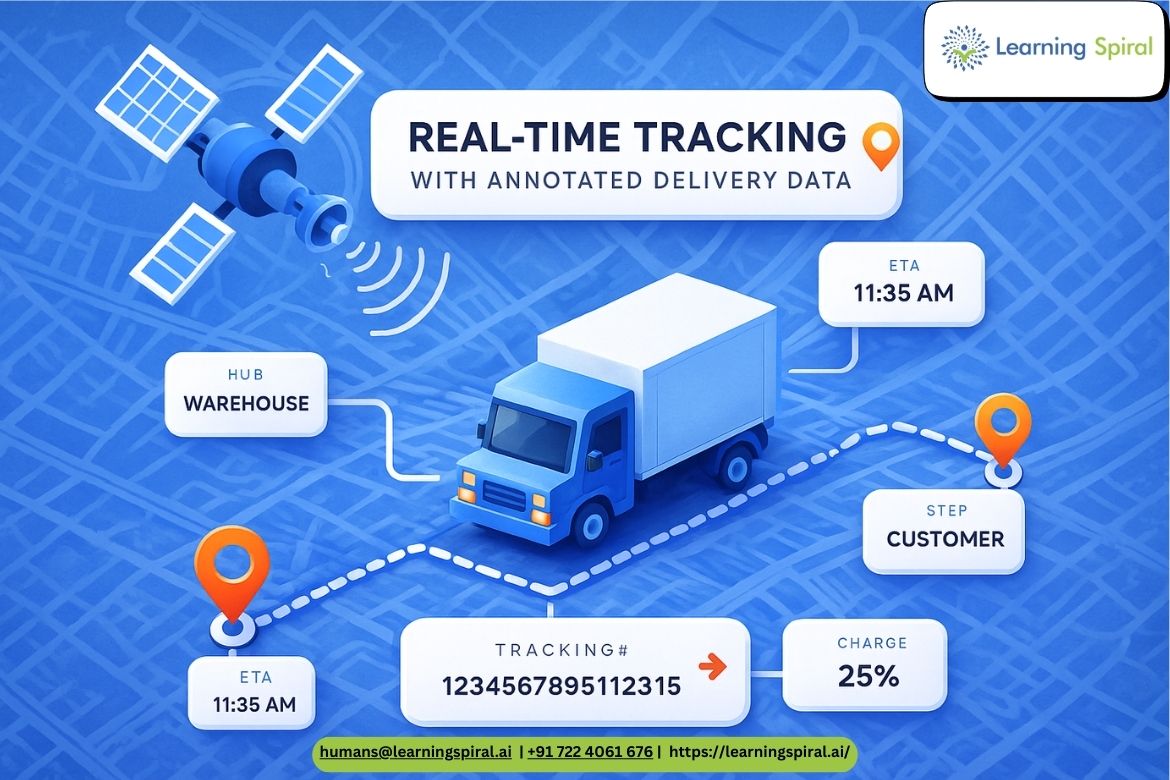
LiDAR provides detailed 3D point clouds that offer precise depth perception and spatial measurements. It’s especially valuable in low-light or night conditions, where visual clarity is limited. Annotating LiDAR data typically involves 3D bounding boxes, segmentation, and sometimes sensor fusion, making it a technically challenging but rewarding process.
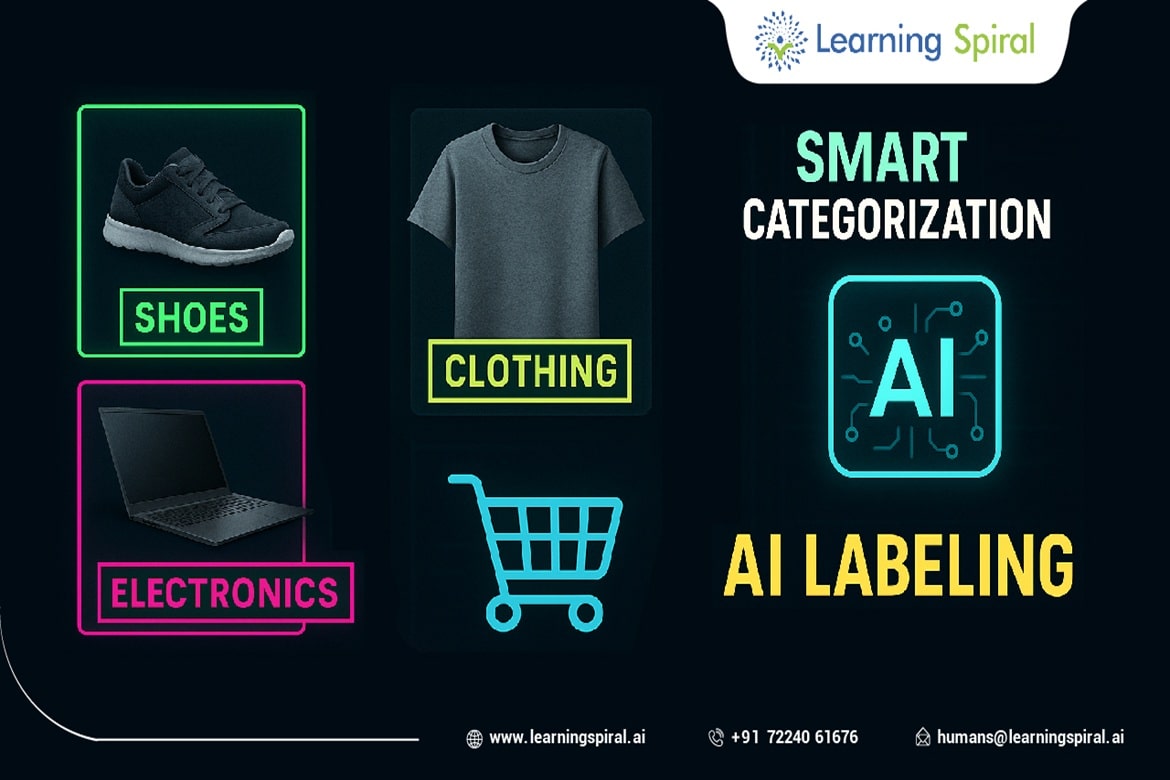
On the other hand, camera data captures color, texture, and environmental context. It’s more intuitive for human annotators and is often used for image annotation, object detection, semantic segmentation, and lane detection. Cameras are cost-effective and offer high-resolution imagery but can be affected by lighting conditions and obstructions.
For robust AI models in autonomous vehicles, combining both LiDAR and camera data—along with high-quality data labeling—creates a more complete understanding of the driving environment. This is where skilled annotation teams come into play.
At Learning Spiral AI, we specialize in delivering comprehensive data annotation services for industries like autonomous driving, robotics, and smart surveillance. Our experts are trained in handling both LiDAR annotation and camera-based image labeling, ensuring accuracy, consistency, and scalability across large datasets.
We use cutting-edge annotation tools and rigorous quality checks to support use cases such as 3D object detection, semantic segmentation, bounding box annotation, and more. With a strong understanding of multi-sensor data, Learning Spiral AI enables AI models to see, sense, and act with greater precision.
As the autonomous future accelerates, accurate annotation of both LiDAR and camera data will remain the foundation of innovation—and Learning Spiral AI is here to lead that journey.